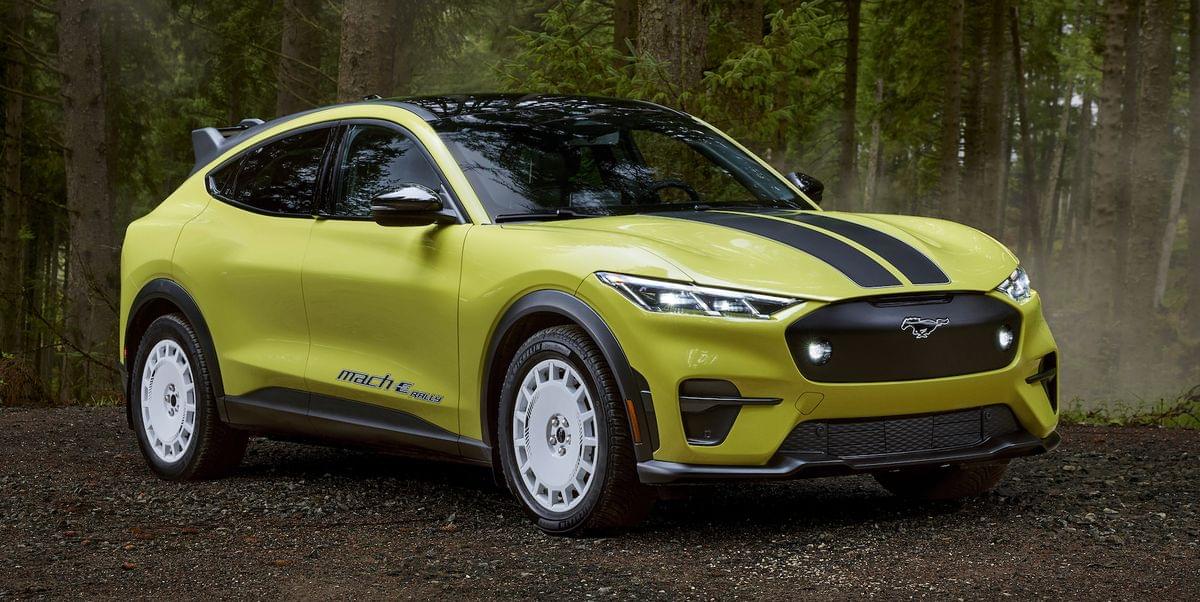
Mustang Mach-E 2024 with all variants Mustang Mach-E Select The Mustang Mach-E Select is the entry-level trim of Ford’s all-electric SUV, offering a blend of performance, range, and affordability. Launched in [insert launch date], the Mach-E Select is designed to appeal to buyers seeking an electric vehicle (EV) with practicality and style. Specifications: Electric Range: [insert range] Acceleration (0-60 mph): [insert acceleration] Horsepower: [insert horsepower] Torque: [insert torque] Seating Capacity: [insert seating capacity] Cargo Space: [insert cargo space] Features: Standard 15.5-inch touchscreen infotainment system with Ford’s SYNC 4A software LED headlights and taillights Keyless entry and push-button start Ford Co-Pilot360 suite of driver-assistance features Heated front seats FordPass smartphone app connectivity for remote vehicle control and monitoring Comparison: Compared to higher trim levels, the Mach-E Select offers a more budget-friendly option for consumers while still providing essential features and capabilities. While it may lack some of the premium amenities of upper trims, it delivers a compelling balance of performance and value. Mustang Mach-E Premium The Mustang Mach-E Premium builds upon the Select trim with additional luxury and technology features, making it an attractive choice for buyers seeking a more refined driving experience. Launched in [insert launch date], the Mach-E Premium offers enhanced comfort, convenience, and performance. Specifications: Electric Range: [insert range] Acceleration (0-60 mph): [insert acceleration] Horsepower: [insert horsepower] Torque: [insert torque] Seating Capacity: [insert seating capacity] Cargo Space: [insert cargo space] Features: Upgraded interior materials and finishes Panoramic sunroof 10-speaker Bang & Olufsen sound system Power-adjustable front seats with memory settings Hands-free power liftgate Available advanced driver-assistance features such as adaptive cruise control and parking assist Comparison: The Mach-E Premium offers a significant step up in luxury and technology compared to the Select trim. With its premium sound system, panoramic sunroof, and additional driver-assistance features, it provides a more upscale driving experience for those willing to invest in added comfort and convenience. Mustang Mach-E California Route 1 Named after the iconic coastal highway, the Mustang Mach-E California Route 1 variant is designed for long-distance cruising and adventure. Launched in [insert launch date], this trim emphasizes range and comfort, making it an ideal choice for road trips and daily commuting alike. Specifications: Electric Range: [insert range] Acceleration (0-60 mph): [insert acceleration] Horsepower: [insert horsepower] Torque: [insert torque] Seating Capacity: [insert seating capacity] Cargo Space: [insert cargo space] Features: Extended-range battery for maximum driving distance Comfort-focused suspension tuning Heated steering wheel and front seats Enhanced navigation system with EV-specific route planning Hands-free power liftgate Unique exterior badging and styling elements Comparison: The Mach-E California Route 1 prioritizes range and comfort, making it an excellent option for buyers who value long-distance driving capabilities and a refined interior experience. While it may lack some of the luxury features of higher trims, its focus on practicality and efficiency makes it an attractive choice for adventure-seekers. Mustang Mach-E GT For buyers seeking exhilarating performance and dynamic driving capabilities, the Mustang Mach-E GT is the ultimate expression of Ford’s electric SUV. Launched in [insert launch date], the Mach-E GT combines sports car-like acceleration with the versatility and practicality of an SUV, delivering an electrifying driving experience. Specifications: Electric Range: [insert range] Acceleration (0-60 mph): [insert acceleration] Horsepower: [insert horsepower] Torque: [insert torque] Seating Capacity: [insert seating capacity] Cargo Space: [insert cargo space] Features: Performance-oriented dual-motor all-wheel-drive system Sport-tuned suspension with MagneRide damping technology Performance brakes and 20-inch alloy wheels Sport seats with bolstering for added support during spirited driving Unique exterior styling elements, including a rear spoiler and diffuser Available performance package with track-focused enhancements Comparison: The Mach-E GT stands out as the high-performance variant of the lineup, offering blistering acceleration and dynamic handling capabilities. With its sports car-inspired design and track-ready features, it appeals to enthusiasts looking for an electrifying driving experience without compromising on practicality or versatility. In conclusion, the Mustang Mach-E lineup offers a diverse range of variants to suit different preferences and driving needs. Whether you prioritize affordability, luxury, range, or performance, there’s a Mach-E model that’s tailored to your preferences. With its sleek design, advanced technology features, and zero-emission performance, the Mustang Mach-E is poised to redefine the electric SUV segment and usher in a new era of sustainable driving.
READ MOREIn the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles (EVs), the Chevrolet Bolt EV stands out as a pioneering model that has reshaped the way we perceive sustainable transportation. Launched in [year of launch], the Bolt EV represents Chevrolet’s commitment to innovation, efficiency, and accessibility, offering consumers an affordable and practical alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the features, benefits, and performance of the Chevrolet Bolt EV to help prospective buyers make an informed decision. Unveiling the Chevrolet Bolt EV: Introduced to the market in [year of launch], the Chevrolet Bolt EV quickly gained attention for its impressive range, spacious interior, and futuristic design. As one of the first affordable long-range electric vehicles available to consumers, the Bolt EV signaled a significant milestone in the transition towards a sustainable automotive future. Its launch marked a pivotal moment in Chevrolet’s history, solidifying the brand’s position as a leader in electric mobility. Key Features and Specifications: At the heart of the Chevrolet Bolt EV is its advanced electric powertrain, consisting of a high-capacity battery pack and a powerful electric motor. With an EPA-estimated range of over 200 miles on a single charge, the Bolt EV offers practicality and convenience for daily commuting, errands, and weekend getaways. Additionally, its fast-charging capabilities enable drivers to replenish the battery quickly, minimizing downtime and maximizing driving time. The Bolt EV’s spacious and versatile interior sets it apart from other electric vehicles in its class. Despite its compact exterior dimensions, the Bolt EV boasts ample headroom, legroom, and cargo space, making it suitable for families, commuters, and outdoor enthusiasts alike. Fold-flat rear seats further enhance the vehicle’s cargo-carrying capacity, allowing for easy transportation of bulky items such as luggage, sports equipment, or groceries. In terms of technology and connectivity, the Chevrolet Bolt EV offers a host of innovative features designed to enhance the driving experience. An intuitive infotainment system with a responsive touchscreen display provides access to navigation, entertainment, and smartphone integration, ensuring that drivers stay connected and entertained on the road. Additionally, advanced driver-assistance systems such as lane-keeping assist, forward collision warning, and automatic emergency braking help enhance safety and peace of mind for both drivers and passengers. Benefits of Driving the Chevrolet Bolt EV: The Chevrolet Bolt EV offers a multitude of benefits that appeal to a wide range of consumers, including: Environmental Sustainability: With zero tailpipe emissions and reduced reliance on fossil fuels, the Bolt EV helps mitigate air pollution and combat climate change, making it an environmentally responsible choice for eco-conscious drivers. Cost Savings: Electric vehicles typically have lower operating costs compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars, thanks to their higher energy efficiency and reduced maintenance requirements. Additionally, incentives and tax credits for EVs can further reduce the total cost of ownership for Bolt EV owners. Convenience and Practicality: With its long-range capability and fast-charging infrastructure, the Bolt EV offers the convenience and flexibility needed for everyday driving. Whether commuting to work, running errands, or embarking on road trips, the Bolt EV provides a seamless and enjoyable driving experience. Advanced Technology: From its advanced electric powertrain to its cutting-edge infotainment system, the Bolt EV incorporates state-of-the-art technology to deliver a modern and connected driving experience. Features such as remote vehicle monitoring, over-the-air software updates, and wireless smartphone charging further enhance convenience and functionality. Driving Dynamics: Despite its eco-friendly credentials, the Bolt EV doesn’t compromise on performance. With instant torque delivery and responsive handling, this electric hatchback offers a spirited driving experience that’s both engaging and enjoyable. The Chevrolet Bolt EV represents a significant step forward in the evolution of electric mobility, offering consumers an affordable, practical, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. With its impressive range, spacious interior, advanced technology, and driving dynamics, the Bolt EV has earned its place as a frontrunner in the electric vehicle market. Whether you’re a first-time EV buyer or a seasoned enthusiast, the Chevrolet Bolt EV is sure to impress with its blend of efficiency, innovation, and style.
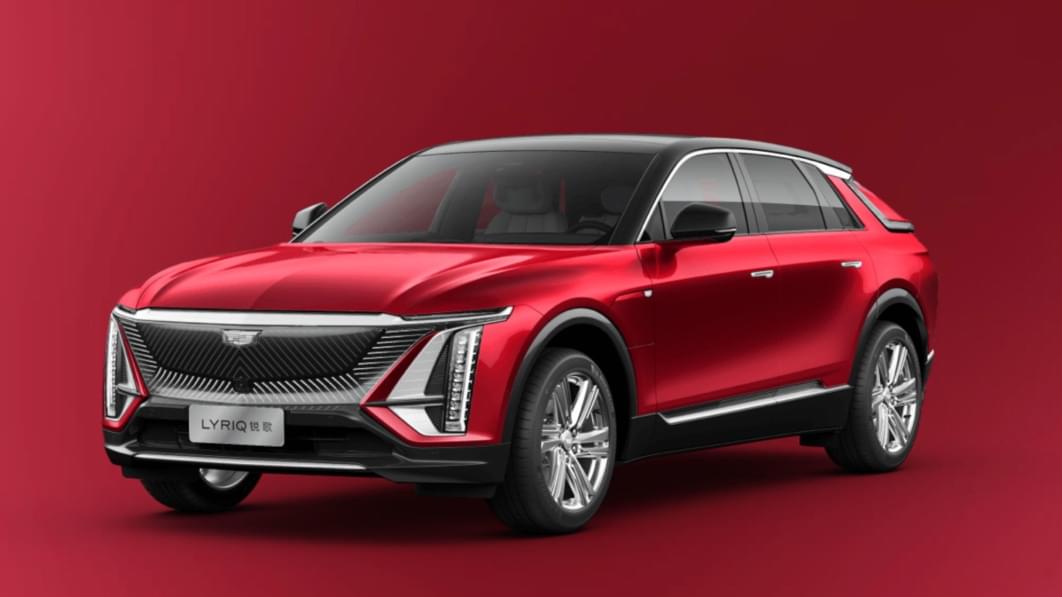
READ MOREIn an automotive landscape that is rapidly evolving towards electrification and sustainable mobility, the Cadillac Lyriq 2024 emerges as a trailblazer, combining cutting-edge technology, luxurious design, and zero-emission driving. As Cadillac’s first all-electric vehicle, the Lyriq represents a significant milestone in the brand’s history, offering buyers a glimpse into the future of automotive innovation. Exterior Design: The Cadillac Lyriq 2024 is a testament to Cadillac’s commitment to bold and distinctive design. From its sleek and sculpted body lines to its striking LED headlights and illuminated grille, the Lyriq exudes an aura of modernity and sophistication. Its aerodynamic shape not only enhances efficiency but also lends the vehicle a sense of dynamic elegance on the road. Interior Comfort and Technology: Step inside the Cadillac Lyriq, and you’re greeted by a spacious and meticulously crafted interior that prioritizes both comfort and technology. Premium materials such as leather upholstery, authentic wood trim, and brushed metal accents adorn the cabin, creating an ambiance of refined luxury. The Lyriq’s panoramic glass roof floods the interior with natural light, while customizable ambient lighting sets the mood for any journey. Technologically, the Lyriq is equipped with Cadillac’s latest infotainment system, featuring a massive curved OLED display that seamlessly integrates navigation, entertainment, and vehicle settings. Advanced driver-assistance features such as Super Cruise, Cadillac’s hands-free driving technology, provide enhanced safety and convenience on the road, allowing drivers to navigate highways with greater confidence. Electric Powertrain and Performance: Underneath its stylish exterior lies the heart of the Cadillac Lyriq: a state-of-the-art electric powertrain that delivers exhilarating performance and seamless acceleration. Powered by Ultium battery technology, the Lyriq offers impressive range on a single charge, making it suitable for both daily commuting and long-distance travel. With instant torque and responsive handling, the Lyriq delivers a thrilling driving experience that’s as exhilarating as it is efficient. Benefits of Driving the Cadillac Lyriq 2024: The Cadillac Lyriq 2024 offers a myriad of benefits that appeal to discerning buyers seeking a combination of luxury, performance, and sustainability: Zero-Emission Driving: As an all-electric vehicle, the Lyriq produces zero tailpipe emissions, helping to reduce air pollution and combat climate change. By driving the Lyriq, buyers can contribute to a cleaner and greener future while enjoying the benefits of electric mobility. Luxurious Comfort: With its spacious interior, premium materials, and advanced technology, the Lyriq offers a first-class travel experience for drivers and passengers alike. Whether navigating city streets or embarking on a long-distance journey, the Lyriq provides a serene and comfortable environment that’s conducive to relaxation and enjoyment. Cutting-Edge Technology: From its curved OLED display to its Super Cruise hands-free driving technology, the Lyriq is packed with innovative features that enhance safety, convenience, and connectivity. With seamless smartphone integration, over-the-air software updates, and advanced driver-assistance systems, the Lyriq sets a new standard for automotive technology and connectivity. Efficiency and Range: Equipped with Ultium battery technology, the Lyriq offers impressive range on a single charge, making it suitable for a wide range of driving scenarios. Whether commuting to work or embarking on a weekend getaway, the Lyriq provides ample range to meet the needs of modern drivers, with the added convenience of fast-charging capabilities for quick refueling stops. Distinctive Design: With its bold styling and sleek proportions, the Lyriq stands out from the crowd, commanding attention wherever it goes. Its aerodynamic shape not only enhances efficiency but also contributes to its dynamic performance on the road, making the Lyriq as eye-catching as it is eco-friendly. The Cadillac Lyriq 2024 represents a bold step forward for Cadillac and the automotive industry as a whole. With its luxurious design, advanced technology, and zero-emission driving capabilities, the Lyriq offers buyers a compelling combination of style, performance, and sustainability. Whether you’re drawn to its striking exterior, its opulent interior, or its cutting-edge features, the Lyriq is sure to impress even the most discerning buyers looking to embrace the future of electric mobility.
READ MOREAs the automotive industry continues its relentless march toward electrification, BMW stands at the forefront of innovation with the introduction of the BMW i7 2024. This flagship luxury sedan represents the pinnacle of BMW’s commitment to sustainability, performance, and cutting-edge technology. With its striking design, advanced features, and zero-emission driving capabilities, the BMW i7 2024 is poised to redefine the luxury electric vehicle segment. Design and Exterior: From the moment you lay eyes on the BMW i7 2024, it’s clear that this is no ordinary sedan. The i7 boasts a sleek and aerodynamic silhouette, punctuated by BMW’s signature kidney grille, sleek LED headlights, and sculpted lines that exude sophistication and elegance. Available in a range of eye-catching colors and finishes, the i7 commands attention on the road while setting a new standard for luxury electric vehicles. Interior Comfort and Technology: Step inside the BMW i7 2024, and you’re greeted by a sumptuous interior that blends luxury with sustainability. Premium materials such as fine leather, sustainable wood trim, and recycled plastics adorn the cabin, creating an ambiance of opulence and refinement. Ergonomically designed seats provide unparalleled comfort for both driver and passengers, while innovative features such as BMW’s Intelligent Personal Assistant and Gesture Control ensure a seamless and intuitive driving experience. Technologically, the i7 is packed with an array of cutting-edge features designed to enhance convenience, connectivity, and safety. The latest iteration of BMW’s iDrive infotainment system offers a user-friendly interface, seamless smartphone integration, and access to a host of digital services and applications. Additionally, advanced driver-assistance systems such as adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automated parking further elevate the driving experience and provide peace of mind on every journey. Electric Powertrain and Performance: At the heart of the BMW i7 2024 lies a state-of-the-art electric powertrain that delivers electrifying performance without compromising on efficiency. Powered by a high-capacity battery pack and dual electric motors, the i7 boasts impressive acceleration, responsive handling, and whisper-quiet operation. With instant torque delivery and precise power management, the i7 offers a dynamic driving experience that’s both exhilarating and refined. Despite its performance credentials, the i7 prioritizes sustainability and environmental responsibility. With zero tailpipe emissions and a commitment to using responsibly sourced materials throughout its construction, the i7 represents BMW’s vision for a greener and more sustainable future. Whether navigating city streets or embarking on long-distance journeys, the i7 delivers uncompromising performance while minimizing its impact on the planet. Benefits of Driving the BMW i7 2024: The BMW i7 2024 offers a myriad of benefits that appeal to discerning buyers seeking a luxury vehicle with a conscience. Some of the key benefits include: Environmental Sustainability: By opting for an all-electric vehicle, drivers can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a cleaner and greener future. With zero tailpipe emissions and a commitment to sustainable manufacturing practices, the i7 embodies BMW’s dedication to environmental stewardship. Cutting-Edge Technology: From its advanced electric powertrain to its intuitive infotainment system, the i7 is packed with state-of-the-art technology designed to enhance comfort, convenience, and safety. With features such as autonomous driving capabilities, augmented reality navigation, and over-the-air software updates, the i7 sets a new standard for luxury electric vehicles. Exceptional Performance: Despite its eco-friendly credentials, the i7 doesn’t compromise on performance. With instant acceleration, precise handling, and a smooth and refined ride, the i7 offers a driving experience that’s both exhilarating and effortless. Whether navigating city streets or cruising down the highway, the i7 delivers performance that’s as impressive as it is sustainable. Luxury and Comfort: With its meticulously crafted interior, cutting-edge technology, and refined driving dynamics, the i7 offers a first-class travel experience for driver and passengers alike. From its spacious and comfortable cabin to its array of premium amenities, the i7 redefines what it means to drive in luxury. Long-Distance Capability: Thanks to its high-capacity battery pack and efficient electric powertrain, the i7 offers ample range to meet the needs of most drivers. With fast-charging capabilities and access to a growing network of charging stations, the i7 is well-equipped for long-distance travel, making it the perfect companion for weekend getaways or cross-country road trips. In conclusion, the BMW i7 2024 represents a bold step forward in the evolution of luxury electric vehicles. With its striking design, advanced technology, and uncompromising performance, the i7 sets a new standard for what’s possible in the world of electric mobility. Whether you’re drawn to its environmental credentials, cutting-edge features, or luxurious amenities, the i7 offers a compelling choice for buyers seeking a premium electric sedan that’s as sustainable as it is stylish.
READ MOREThe Audi Q8 e-tron represents the pinnacle of luxury, performance, and sustainability in the realm of electric SUVs. Combining Audi’s signature craftsmanship with cutting-edge electric technology, the Q8 e-tron offers a premium driving experience that is both exhilarating and eco-friendly. In this detailed review, we’ll delve into the features, interior, exterior, benefits, mileage, and more of the Audi Q8 e-tron. Exterior Design: The Audi Q8 e-tron boasts a striking and dynamic exterior design that seamlessly blends sportiness with sophistication. Its sleek lines, sculpted body panels, and bold proportions create a commanding presence on the road. The front fascia is characterized by Audi’s signature Singleframe grille, flanked by sleek LED headlights with intricate lighting signatures. The sculpted hood and muscular wheel arches convey a sense of athleticism, while the sloping roofline adds a touch of elegance to the overall profile. At the rear, LED taillights with dynamic turn signals emphasize the Q8 e-tron’s modern aesthetic, while the integrated spoiler enhances aerodynamic efficiency. Interior Comfort and Luxury: Step inside the Audi Q8 e-tron, and you’ll be greeted by a luxurious and futuristic cabin that exudes refinement and sophistication. Premium materials such as leather, wood, and aluminum adorn the interior, while attention to detail is evident in every aspect of the design. The spacious and ergonomically designed seats provide excellent comfort and support for long journeys, while the panoramic sunroof floods the cabin with natural light, creating an airy and inviting atmosphere. Ambient lighting sets the mood for every drive, allowing you to customize the interior ambiance to suit your preferences. Technological Innovations: The Audi Q8 e-tron is equipped with a plethora of advanced technological features that enhance convenience, safety, and entertainment. The centerpiece of the cockpit is the MMI touch response system, which consists of dual touchscreens that control various functions such as navigation, infotainment, and climate control. Audi’s virtual cockpit, a fully digital instrument cluster, provides customizable displays of relevant information, ensuring that vital data is always at your fingertips. Additionally, the Q8 e-tron offers a suite of driver assistance systems, including adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automatic emergency braking, which enhance safety and confidence behind the wheel. Electric Performance: Underneath its sleek exterior, the Audi Q8 e-tron harnesses the power of electrification to deliver exhilarating performance with zero emissions. The heart of the Q8 e-tron is its advanced electric drivetrain, which consists of powerful electric motors mounted on each axle, providing instantaneous torque and seamless acceleration. The Quattro all-wheel-drive system ensures optimal traction and stability in all driving conditions, while Audi’s adaptive air suspension delivers a smooth and composed ride quality. With multiple driving modes to choose from, including an eco-friendly electric mode, the Q8 e-tron offers a versatile driving experience that can be tailored to suit your preferences. Range and Charging: One of the key benefits of the Audi Q8 e-tron is its impressive range and fast-charging capabilities, allowing you to travel long distances with confidence and convenience. The Q8 e-tron is equipped with a high-capacity lithium-ion battery pack that provides ample range on a single charge, ensuring that range anxiety is a thing of the past. Additionally, Audi’s extensive network of fast-charging stations enables rapid recharging, allowing you to replenish the battery quickly and get back on the road in no time. Whether you’re commuting to work or embarking on a cross-country road trip, the Q8 e-tron offers the range and flexibility to meet your needs. Environmental Benefits: By opting for the Audi Q8 e-tron, you’re not just investing in a luxury SUV – you’re also making a positive impact on the environment. With zero tailpipe emissions, the Q8 e-tron helps reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier planet. Additionally, the use of renewable energy sources for charging further reduces the carbon footprint of the vehicle, making it a sustainable choice for eco-conscious drivers. By embracing electric mobility, Audi is leading the way towards a greener and more sustainable future, without compromising on performance or luxury. The Audi Q8 e-tron is a testament to Audi’s commitment to innovation, luxury, and sustainability. With its striking design, luxurious interior, advanced technology, electrifying performance, impressive range, and environmental benefits, the Q8 e-tron offers a compelling package that sets it apart in the competitive luxury SUV segment. Whether you’re drawn to its cutting-edge features, eco-friendly credentials, or simply the thrill of electric driving, the Audi Q8 e-tron represents the future of automotive excellence.
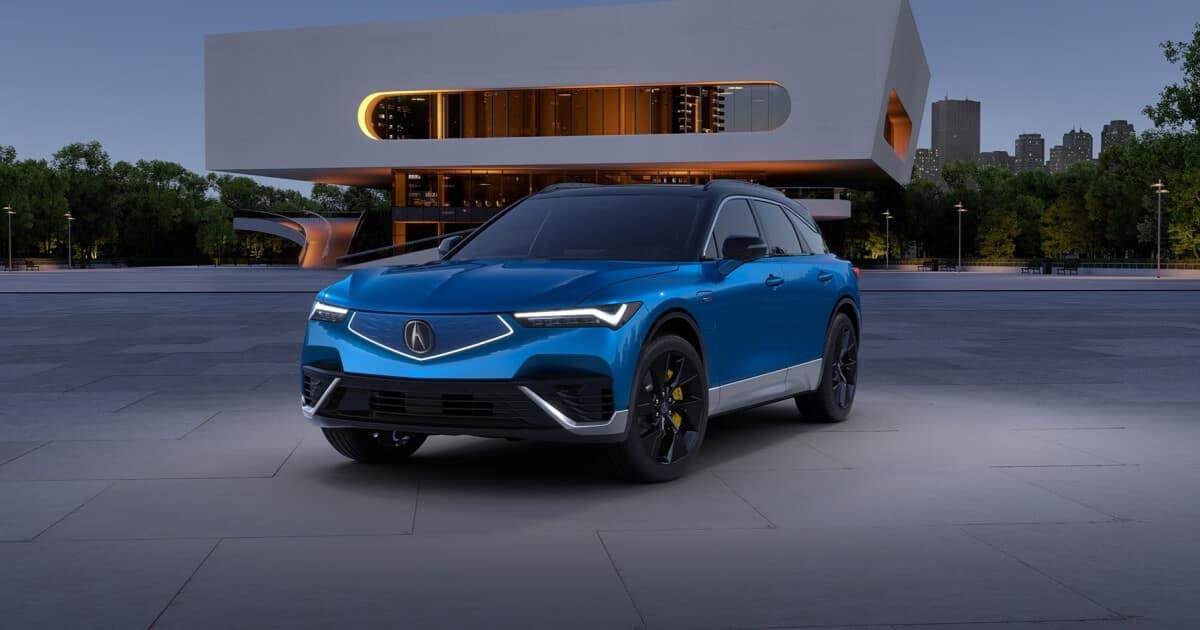
READ MOREThe Acura All-Electric ZDX marks a significant milestone in the automotive industry, combining cutting-edge technology with luxurious design to deliver an unparalleled electric driving experience. In this 1000-word exploration, we delve into the features, interior, exterior, benefits, mileage, and more of this groundbreaking vehicle. Features: Electric Powertrain: At the heart of the Acura All-Electric ZDX is its advanced electric powertrain, which replaces traditional internal combustion engines with electric motors powered by high-capacity battery packs. This setup not only eliminates tailpipe emissions but also provides instant torque for exhilarating acceleration. All-Wheel Drive (AWD): Equipped with an intelligent all-wheel-drive system, the All-Electric ZDX delivers enhanced traction and stability, ensuring confident handling in various road conditions. The AWD system intelligently distributes power to each wheel, optimizing performance and efficiency. Regenerative Braking: The Acura All-Electric ZDX features regenerative braking technology, which captures kinetic energy during deceleration and converts it into electricity to recharge the battery. This system not only improves energy efficiency but also helps to extend driving range. Advanced Safety Features: Safety is paramount in the All-Electric ZDX, with a suite of advanced driver-assistance features designed to provide peace of mind on every journey. These include adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, forward collision warning, and automatic emergency braking. Infotainment System: Inside the cabin, occupants are treated to a state-of-the-art infotainment system, featuring a large touchscreen display with support for smartphone integration, navigation, voice commands, and a premium sound system for an immersive audio experience. Interior: Luxurious Comfort: Step inside the Acura All-Electric ZDX, and you’ll be greeted by a spacious and meticulously crafted interior designed to provide the utmost comfort for all passengers. Premium materials such as leather upholstery, wood trim, and brushed aluminum accents create a refined ambiance. Versatile Seating: With seating for up to five passengers, the All-Electric ZDX offers ample room for everyone to stretch out and relax. The versatile rear seats can be folded down to expand cargo space, accommodating larger items with ease. Advanced Climate Control: Dual-zone automatic climate control ensures that occupants stay comfortable, with individual temperature settings for the driver and front passenger. Additionally, heated and ventilated seats provide customizable comfort, regardless of the weather outside. Exterior: Sleek Design: The Acura All-Electric ZDX boasts a sleek and aerodynamic design that not only enhances its visual appeal but also improves efficiency and performance. From its sculpted lines to its bold grille and LED headlights, every aspect of the exterior is crafted with precision and attention to detail. Panoramic Sunroof: Let natural light flood the cabin with the available panoramic sunroof, which extends across the entire roof of the vehicle, providing breathtaking views of the sky above. Whether open or closed, the sunroof adds an extra touch of luxury to the All-Electric ZDX. Integrated Charging Port: Located discreetly within the front grille, the integrated charging port allows for convenient access when recharging the battery. This seamless design element not only adds to the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal but also underscores its electric capabilities. Benefits: Environmental Sustainability: As an all-electric vehicle, the Acura ZDX contributes to a cleaner and greener future by producing zero tailpipe emissions. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, it helps to mitigate air pollution and combat climate change, making it an eco-friendly choice for environmentally conscious drivers. Lower Operating Costs: With fewer moving parts and no need for gasoline, the All-Electric ZDX offers lower operating costs compared to traditional gas-powered vehicles. Maintenance expenses are also reduced, resulting in long-term savings for owners. Instant Torque: Electric motors deliver instant torque, providing immediate acceleration and responsive performance that rivals or exceeds that of traditional combustion engines. This translates to a thrilling driving experience with seamless power delivery. Mileage: Range: The Acura All-Electric ZDX offers an impressive range on a single charge, allowing drivers to travel farther without needing to recharge. With advancements in battery technology, range anxiety becomes a thing of the past, giving drivers the confidence to explore new destinations. Charging Options: Charging the All-Electric ZDX is convenient and hassle-free, thanks to a variety of charging options available to drivers. Whether using a standard home outlet, a Level 2 charging station, or a fast DC charger, recharging the battery is quick and easy, allowing for maximum flexibility and convenience. The Acura All-Electric ZDX represents the future of automotive innovation, combining advanced electric technology with luxury and performance. With its sleek design, spacious interior, and eco-friendly credentials, it offers a compelling alternative to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, setting a new standard for electric luxury SUVs. Whether cruising through city streets or embarking on long-distance journeys, the All-Electric ZDX delivers an unparalleled driving experience that is as exhilarating as it is sustainable.
READ MORE10 best luxury electric cars for 2024 in the USA and Canada along with their standout features: Tesla Model S Plaid Best Features: Industry-leading acceleration, advanced Autopilot system, spacious interior with cutting-edge technology, long-range capability. Why It’s Best: Tesla’s continuous innovation in electric vehicle technology sets the Model S Plaid apart, offering unmatched performance and range in the luxury electric car segment. Lucid Air Best Features: Sleek design, luxurious interior with spacious cabin, exceptional range, fast charging capabilities, advanced driver assistance systems. Why It’s Best: Lucid Air combines elegant design with impressive performance and range, appealing to luxury car buyers looking for both style and sustainability. Porsche Taycan Best Features: Porsche’s renowned driving dynamics, premium interior craftsmanship, fast charging capability, available all-wheel drive. Why It’s Best: The Porsche Taycan delivers a thrilling driving experience typical of the brand, while also offering the benefits of electric propulsion, making it a top choice for luxury car enthusiasts. Audi e-tron GT Best Features: Stunning design, high-quality interior materials, smooth acceleration, advanced technology features, available sporty performance variants. Why It’s Best: The Audi e-tron GT combines Audi’s luxury pedigree with electric power, offering a blend of performance, comfort, and cutting-edge technology in a stylish package. Mercedes-Benz EQS Best Features: Luxurious interior with high-tech features, exceptional ride comfort, long-range capability, advanced driver assistance systems. Why It’s Best: The Mercedes-Benz EQS sets new standards for luxury electric vehicles with its opulent interior, smooth driving experience, and impressive electric range, appealing to discerning buyers. BMW iX Best Features: Futuristic design, spacious and well-appointed interior, advanced infotainment system, efficient electric drivetrain, available all-wheel drive. Why It’s Best: The BMW iX combines BMW’s signature luxury with electric performance, offering a premium driving experience with zero emissions in a versatile SUV package. Rivian R1S Best Features: Adventure-ready design, off-road capability, spacious interior with versatile cargo space, long-range capability, available advanced driver assistance systems. Why It’s Best: The Rivian R1S stands out as a luxury electric SUV with rugged capabilities, appealing to buyers looking for an eco-friendly vehicle that can handle outdoor adventures. Jaguar I-PACE Best Features: Distinctive design, sporty performance, luxurious interior, engaging driving dynamics, long-range capability. Why It’s Best: The Jaguar I-PACE offers a blend of Jaguar’s performance heritage with electric power, delivering a thrilling driving experience with zero tailpipe emissions. Volvo XC40 Recharge Best Features: Scandinavian design, comfortable interior with premium materials, advanced safety features, long-range capability, intuitive infotainment system. Why It’s Best: The Volvo XC40 Recharge combines Volvo’s commitment to safety and sustainability with electric power, offering a stylish and practical luxury SUV option. Cadillac Lyriq Best Features: Bold design, spacious interior with advanced technology features, long-range capability, available Super Cruise hands-free driving system. Why It’s Best: The Cadillac Lyriq marks Cadillac’s entry into the luxury electric vehicle market with a combination of striking design, advanced technology, and impressive electric range, catering to luxury car buyers seeking style and innovation. These luxury electric cars offer a range of features and capabilities, from performance and design to technology and sustainability, making them the top choices for discerning buyers in 2024.
READ MOREAnalysis of the Top 10 Best-Selling Electric Vehicles in the US and Canada in 2023 The year 2023 witnessed a significant surge in the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in the United States and Canada, fueled by growing environmental consciousness, technological advancements, and governmental incentives. In this analysis, we delve into the top 10 best-selling electric vehicles in both countries, shedding light on their features, market performance, and factors contributing to their popularity. Tesla Model 3: Retaining its position as a frontrunner in the EV market, the Tesla Model 3 continued to dominate sales in 2023. Renowned for its sleek design, impressive range, and cutting-edge autopilot features, the Model 3 appealed to a wide range of consumers seeking both performance and sustainability. Tesla Model Y: Following closely behind its predecessor, the Tesla Model Y secured a prominent spot among the top-selling EVs. With its spacious interior, long-range capabilities, and robust safety features, the Model Y attracted families and adventure enthusiasts alike. Chevrolet Bolt EV: Chevrolet’s Bolt EV maintained its popularity in 2023, offering an affordable yet efficient option for eco-conscious consumers. With its practical design, ample cargo space, and competitive range, the Bolt EV continued to appeal to urban commuters and environmentally aware drivers. Nissan Leaf: As one of the pioneers in the electric vehicle market, the Nissan Leaf remained a formidable contender in 2023. Boasting a reliable performance, comfortable ride, and user-friendly features, the Leaf appealed to budget-conscious consumers and urban dwellers seeking a sustainable driving option. Ford Mustang Mach-E: Introduced as Ford’s foray into the electric vehicle segment, the Mustang Mach-E garnered significant attention and sales in 2023. With its iconic design, exhilarating performance, and advanced technology, the Mach-E attracted both traditional Mustang enthusiasts and new adopters of electric mobility. Volkswagen ID.4: Volkswagen’s ID.4 made waves in the EV market, offering a blend of practicality, versatility, and German engineering. With its spacious interior, impressive range, and sleek design, the ID.4 appealed to drivers looking for a reliable electric SUV with a touch of European flair. Audi e-tron: Audi’s e-tron continued to captivate consumers with its luxurious amenities, refined driving experience, and cutting-edge technology. As one of the leading luxury electric SUVs, the e-tron appealed to discerning buyers seeking premium comfort and performance without compromising on sustainability. Hyundai Kona Electric: Hyundai’s Kona Electric emerged as a top choice for value-conscious consumers, offering an affordable yet feature-packed electric crossover. With its efficient powertrain, generous cargo space, and extensive standard features, the Kona Electric appealed to practical-minded drivers seeking an eco-friendly driving solution. Kia Niro EV: The Kia Niro EV gained traction in 2023, thanks to its blend of efficiency, versatility, and affordability. With its comfortable interior, commendable range, and comprehensive warranty coverage, the Niro EV appealed to budget-conscious families and urban commuters alike. Porsche Taycan: Porsche’s Taycan represented the epitome of luxury and performance in the electric vehicle market. With its breathtaking acceleration, opulent interior, and state-of-the-art technology, the Taycan catered to affluent buyers seeking an exhilarating driving experience coupled with environmental consciousness. The year 2023 witnessed a remarkable surge in the popularity of electric vehicles in the United States and Canada, with a diverse array of models capturing consumers’ attention and driving significant sales growth. From affordable compact cars to luxurious SUVs and high-performance sports cars, the top 10 best-selling EVs exemplify the industry’s evolution towards sustainable mobility and innovation. As technology continues to advance and infrastructure expands, the electric vehicle market is poised for further growth and transformation in the years to come.
READ MOREIntroduction: Explore the Complete Guide to Installing Tesla Home Chargers, encompassing insights into Tesla Home Charging Stations, available choices, infrastructure prerequisites, installation expenditures, and strategies to economize via EV Life. Tesla’s Pioneering Role in Electric Vehicle Charging: As electric vehicle popularity surges, Tesla stands as a frontrunner in EV innovation. Redefining electric vehicle charging, Tesla integrates superior equipment, innovative technology, a robust network, and reliable performance. Unraveling the Importance of Home Charging with Tesla: Delve into the significance of home charging, why Tesla sets the standard, the installation procedures for Tesla chargers, and the advantages of opting for Tesla for your charging requirements. Tesla Home Charging Options: Battery charging is a pivotal concern for EV drivers. Establishing a home charging station alleviates “range anxiety” and ensures convenient and reliable EV charging from the comfort of your home. Home charging stations prove cheaper, more accessible, and allow for off-peak hour charging, minimizing energy expenses. Levels of Tesla Charging: Tesla offers various charging levels, each operating at distinct voltage levels. Level 1 Charging: Utilizes standard 120V electrical outlets, providing 1.4 kW of power. Level 2 Charging: Utilizes 240V outlets, delivering 3.7-17.2 kW of power. Level 3 Charging (Superchargers): High-powered 480V circuits, delivering up to 250 kW of power. Installing Superchargers at Home: Despite their fast charging capabilities, Superchargers aren’t suitable for home use due to high costs, potential battery degradation, and lack of availability. DIY vs. Professional Installation: Certified Tesla installation technicians can assess your electrical systems, recommend suitable chargers, and conduct installations. The installation process involves standard items and may require additional components for complex setups. Step-by-Step Installation Guide: Before installing a Tesla home charger, evaluate your electrical system, make necessary upgrades, select a suitable location, choose the charger model, purchase the charger, and follow installation instructions meticulously. Saving Money on Tesla Home Charging with EV Life: Numerous federal and state EV incentive programs aid in reducing Tesla charger purchase costs. Power companies also offer rebates for qualified drivers. EV Life provides financing solutions to help maximize savings on electric vehicle purchases and charger installations. Conclusion: Unveil the opportunities to economize on Tesla home charging while contributing to environmental sustainability. Get pre-qualified with EV Life today to discover potential savings on electric vehicles and Tesla home chargers.
READ MOREDiscover the essentials of electric car insurance, from securing favorable deals to cutting costs on your electric vehicle (EV) to counterbalance the higher insurance expenses. As electric cars gain popularity, grasping insurance costs and choices becomes paramount for prospective owners contemplating the switch. Unlike traditional gasoline cars, insuring an EV involves unique factors. This exhaustive handbook delves into electric car insurance intricacies, covering cost determinants, money-saving techniques, and more. Understanding Electric Vehicle Insurance Costs The expense of insuring an electric car can vary significantly due to multiple factors. Typically, premiums for electric car insurance surpass those for conventional gasoline cars. Recent research indicates that insuring an electric vehicle costs around 20% more on average than insuring a gasoline vehicle. However, bear in mind that your electric car insurance cost may fluctuate based on factors like your EV’s make and model, driving history, age, location, and your chosen auto insurance provider. For instance, insuring high-end luxury EV models such as the Tesla Model X or Rivian R1S might be notably pricier than insuring more economical options like the Nissan LEAF or Chevrolet Bolt EV. Understanding the Elevated Costs of Electric Vehicle Insurance Several factors contribute to the higher insurance costs associated with electric vehicles compared to their gasoline counterparts: Higher Repair Expenses: Electric vehicles often necessitate specialized equipment and trained technicians for repairs, which can inflate costs compared to traditional vehicles. Battery Replacement Costs: Replacing the battery pack in an electric vehicle can be a costly affair, sometimes running into thousands of dollars. Advanced Technology: Electric cars feature cutting-edge technology like advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and sophisticated electronics, which can be expensive to repair or replace if damaged. Limited Repair Facilities: With electric vehicles still relatively new, there are fewer repair shops equipped to handle EV repairs, potentially resulting in higher costs. Higher Vehicle Value: Many electric cars, especially luxury models, come with higher price tags than their gasoline-powered counterparts, leading to higher insurance premiums. Where to Obtain Electric Car Insurance Most car insurance companies offer electric car insurance, including Geico, Progressive, State Farm, and Allstate. Some insurers, such as Travelers and Liberty Mutual, even provide specialized EV auto insurance rates with unique discounts for electric vehicle owners. When shopping for electric car insurance, it’s crucial to compare quotes from multiple providers and carefully assess coverage options and exclusions. Consider factors such as liability and coverage limits, collision and comprehensive coverage, roadside assistance, and any EV-specific additional options. Tips for Reducing Electric Vehicle Insurance Costs While insuring an electric vehicle may be costlier than traditional cars, employing several strategies can help save money: Comparison Shopping: Compare quotes from various insurance providers to find the best rates and coverage options. Bundling Policies: Many insurers offer discounts for bundling your EV insurance with other policies like home or renters insurance. Maintaining a Clean Driving Record: A clean driving record devoid of accidents and violations can lower insurance premiums. Increasing Deductibles: Raising your insurance deductible can reduce monthly or annual premiums, although consider potential out-of-pocket costs in case of claims. Considering Usage-Based Insurance: Some insurers offer usage-based insurance programs that reward safe driving habits with lower rates. Leveraging Discounts: Many insurers provide discounts for safety features, anti-theft devices, low mileage, and completion of defensive driving courses. Exploring Tesla Auto Insurance Tesla offers its in-house insurance program called Tesla Insurance, tailored specifically for Tesla vehicles. Available in select states, Tesla Insurance aims to provide transparent and competitive insurance by handling claims and repairs directly, without involving an insurance company middleman. However, Tesla’s insurance comes with unique rules affecting insurance rates. Except for California residents, you’re required to use your Tesla’s built-in telematics system, the Tesla Safety Score, which monitors your driving behavior and becomes the primary factor in determining your insurance rates. While conventional insurers consider factors like claims history and driving record, Tesla Insurance heavily relies on real-time driving performance assessed by the Safety Score. This system incentivizes safe driving habits but introduces variability in insurance rates based on recent driving patterns. If you own a Tesla and reside in an area where Tesla Insurance operates, consider this option alongside quotes from traditional insurers. Additional Benefits of Going Electric While insurance considerations are crucial when transitioning to electric, embracing this eco-friendly technology offers numerous advantages beyond insurance rates: Lower Operating Costs: EVs boast lower operating expenses compared to gasoline vehicles, with reduced upkeep costs due to no need for regular oil changes or engine maintenance. Environmental Sustainability: EVs contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality by eliminating tailpipe emissions. High-Performance Driving: EVs provide responsive and exhilarating driving experiences with instant torque and smooth acceleration. Quiet and Comfortable Rides: Electric motors operate quietly, offering a serene cabin environment conducive to comfortable commutes or long journeys. Cutting-Edge Technology: EVs incorporate advanced technologies like ADAS, automated software updates, and expansive infotainment systems, providing the latest automotive innovations. Saving Money on Your EV In addition to insurance rates, various strategies can help save money on your electric vehicle: Tax Credits and Incentives: Federal and state governments offer tax credits, rebates, reduced registration fees, and other incentives to promote EV adoption. Charging at Home: Installing a home charging station can be cost-effective compared to relying solely on public charging stations. Utility Discounts: Some utility companies offer EV rebates, discounted rates, or special charging plans for electric vehicle owners. Maintenance and Fuel Savings: EVs typically require less maintenance than conventional vehicles and offer lower fuel costs due to cheaper charging. By understanding electric vehicle insurance intricacies and exploring cost-saving strategies, you can make informed decisions about owning an EV while minimizing financial impact. To explore the best deal for your preferred electric vehicle, get pre-qualified at EV Life and start saving money while contributing to a sustainable future.
READ MORE